
Welcome to the homepage of the Black Hole Feedback and Cosmic Ray Astrophysics group, an independent research group in Astrophysics Division of Shanghai Astronomical Observatory led by Prof. Fulai Guo. Our group works on theoretical astrophysics, with a focus on numerical simulations. Our research interests cover a broad variety of topics in contemporary astrophysics, including but not limited to
One important topic that we are currently working on is to study the physical mechanism of black hole feedback and its roles in the evolution of galaxies, galaxy groups and clusters. Which black hole accretion and feedback modes are important in galaxy evolution? Whether, when, and how do massive black holes and galaxies co-evolve? How do black holes transfer energy to the interstellar and intracluster media? One important feature of our research is to explore the dynamical roles and observational signatures of cosmic rays in black hole feedback and galactic winds.

Group leader, Professor
fulai(AT)shao.ac.cn

Associate Professor
mcwu(AT)shao.ac.cn


Ph.D. Student
dxd(AT)shao.ac.cn

Ph.D. Student
ruiyuzhang(AT)shao.ac.cn


Ph.D. Student
skxie(AT)shao.ac.cn

MSc Student
mw(AT)shao.ac.cn
PUBLICATIONS AFTER 2015
PUBLICATIONS BEFORE 2015
We are the first to propose and study the well-known AGN Jet Model for the Fermi Bubbles in the Milky Way (Guo & Mathews 2012; Guo et al 2012)
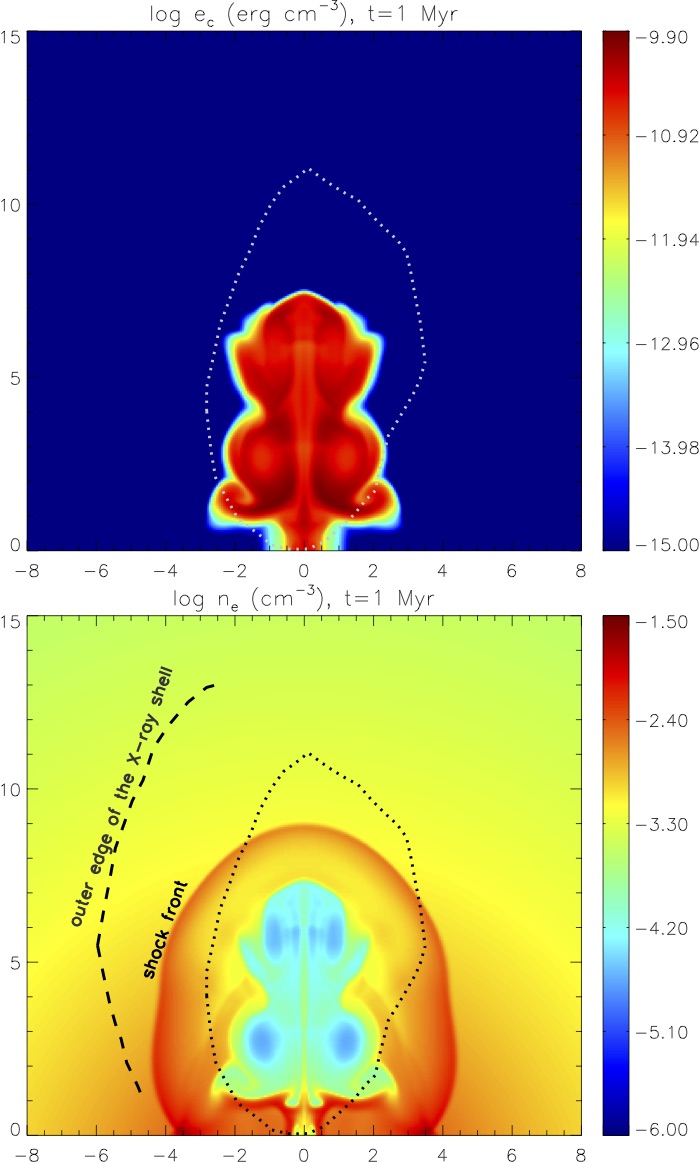
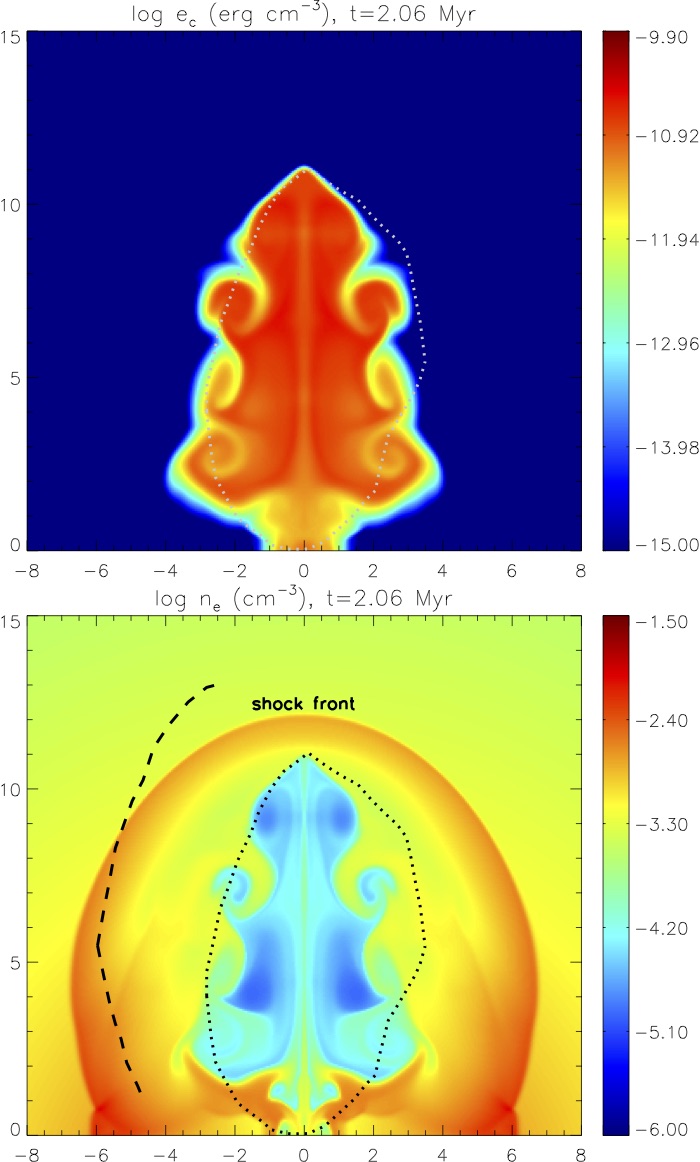
We are the first to demonstrate that cosmic rays from AGN outbursts and the dissipation of hydromagnetic waves induced by the cosmic ray streaming instability may efficiently heat cool cores in galaxy clusters (Guo & Oh 2008)
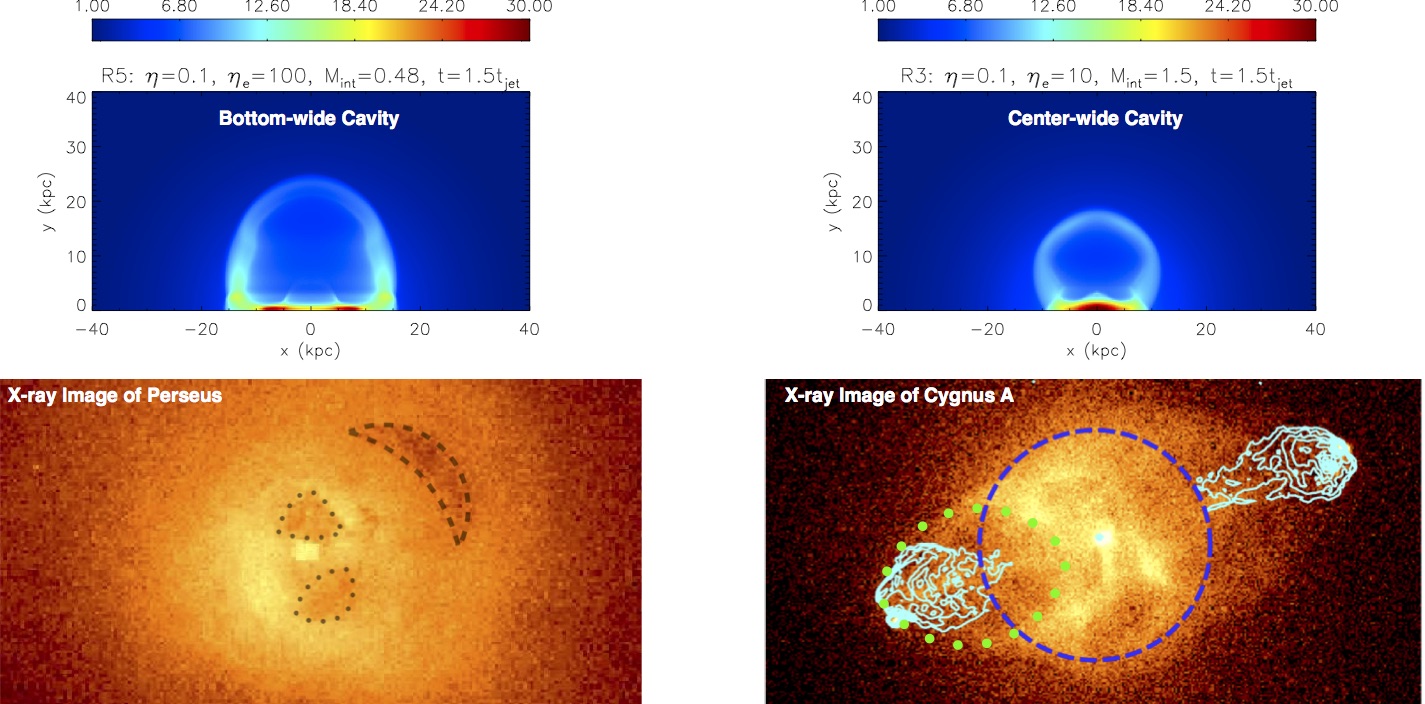
We are the first to propose to study the properties of AGN jets with the shapes of X-ray cavities in galaxy clusters, and to point out the importance of very-light internally-subsonic jets in radio-mode AGN feedback (Guo 2015; Guo 2016)
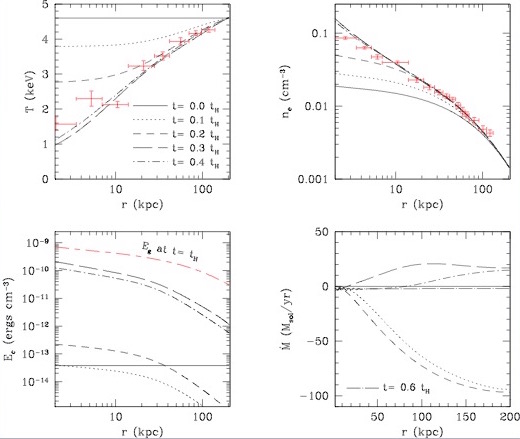
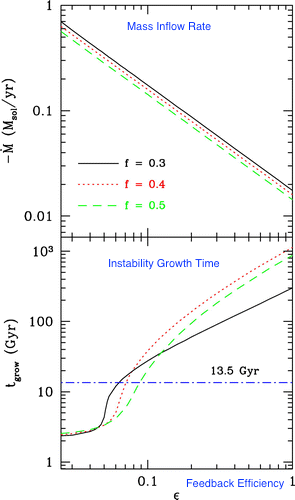
We performed the first and the only to date global stability analysis of galaxy cluster models with AGN feedback, revealing the importance of AGN feedback in clusters (Guo, Oh, & Ruszkowski 2008)
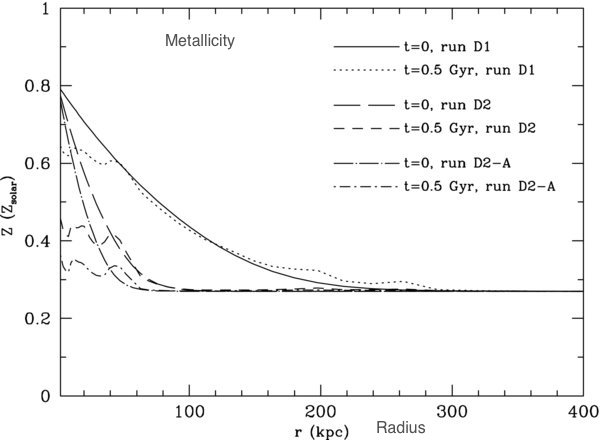
We are the first to argue with hydrodynamic simulatiuons that some powerful AGN outbursts may destroy cool cores in galaxy clusters, producing non-cool-core clusters (Guo & Oh 2009; Guo & Mathews 2010b)

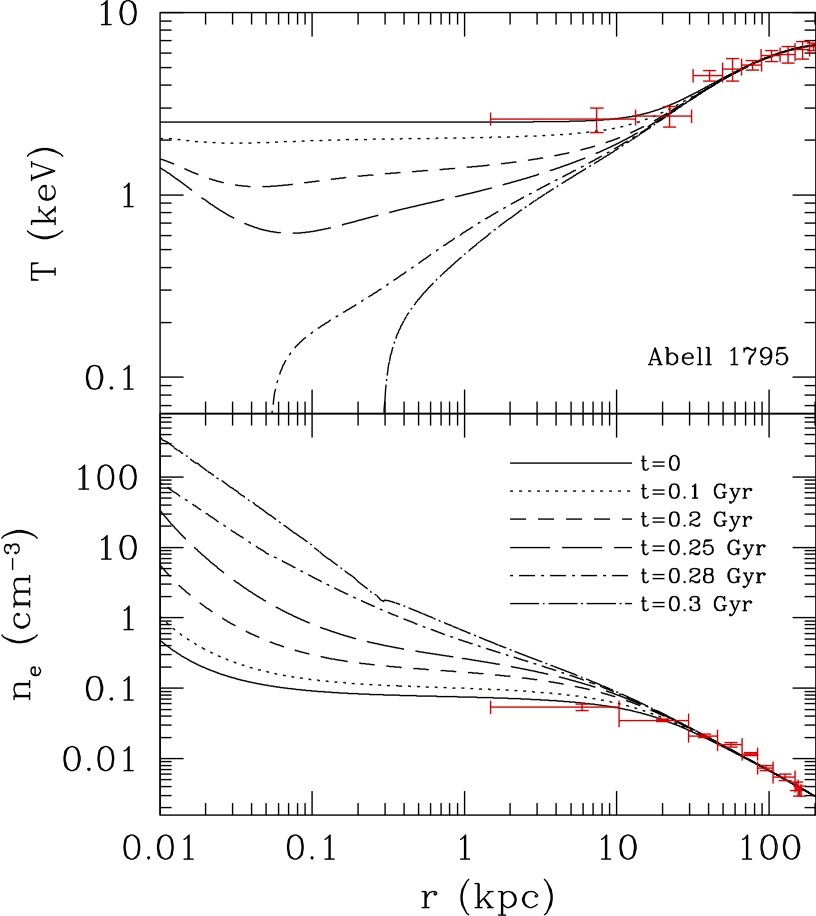
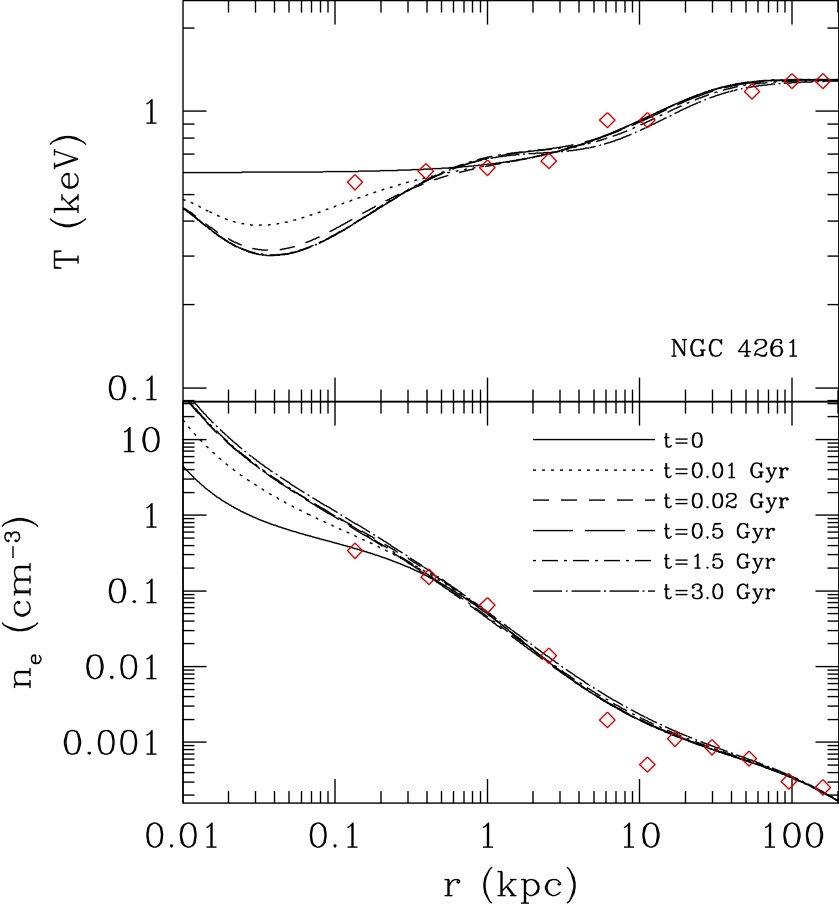
We are the first to show that spherical accretion of cooling flows onto supermassive black holes has two distinct modes: cold mode with fast development of central cooling catastrophe and hot mode with centrally cuspy temperature profiles (Mathews & Guo 2012a; Guo & Mathews 2014; Guo 2014)
Applications are invited for both graduate student and postdoc positions in our group. Both Chinese and international applicants are welcome.
If you are interested in pursuing either Master or Ph.D. degree in our group, please feel free to contact Prof. Guo for more details. Standard financial support in various forms is available. Shanghai Astronomical Observatory usually provides strongly subsidized dormitory housing for graduate students.
本课题组有一些很适合硕士和博士阶段的课题。非常欢迎感兴趣的同学申请加入、保研、或报考我们课题组。我们同时也支持一部分大学生到我们课题组做一些短期项目,包括研究实习与毕业论文。可以随时通过Email联系咨询我们。
Shanghai Astronomical Observatory (SHAO) invites applications for a postdoctoral position in the Black Hole Feedback and Cosmic Ray Astrophysics research group. Applicants should have a good background in theoretical astrophysics, and prior experience in computational simulations is desired. Priority will be given to candidates with an interest in any of the following areas: AGN feedback, galaxy evolution, galactic winds, cosmic ray astrophysics, the circumgalactic medium. Both Chinese and international applicants are encouraged to apply.
The appointment is awarded for two years initially, extendable for up to four years depending on performance and funding availability. The starting date is flexible. The salary is dependent on qualification and experience, and will be highly competitive. Successful candidates have direct access to computer clusters at SHAO (with nearly 3000 cores), and will also be supported to apply for various postdoc fellowships and grants funded by Chinese funding agencies. The position comes with research funds for publications, travel, etc. SHAO provides significantly subsidized dormitory housing on site.
SHAO belongs to the Chinese Academy of Sciences, which provides a diverse setting and research facilities. SHAO has good computer facilities, ample research funds, and an active visitor program. The Astrophysics Division of SHAO has about 40 faculty members, 20 postdocs, and 40 PhD students. SHAO members are actively involved in many important international and domestic projects such as SKA, SDSS-IV, LSST, LAMOST, HXMT, and FAST. More information can be found at http://astro-en.shao.cas.cn.
SHAO is located in downtown Shanghai, one of the most rapidly evolving and cosmopolitan cities in Asia. There are a very large population of international expats living in Shanghai. For an introductory guidance of working at SHAO as an expat, please see this webpage.
Applicants should submit curriculum vitae, publication list, a brief research statement, and arrange for three (or two) reference letters to be sent to fulai@shao.ac.cn by email. Inquiries for the job details are also welcome. Applications will be considered until the position is filled.
Related Links
Helpful Resources
Address
17th Floor, Astronomy Building